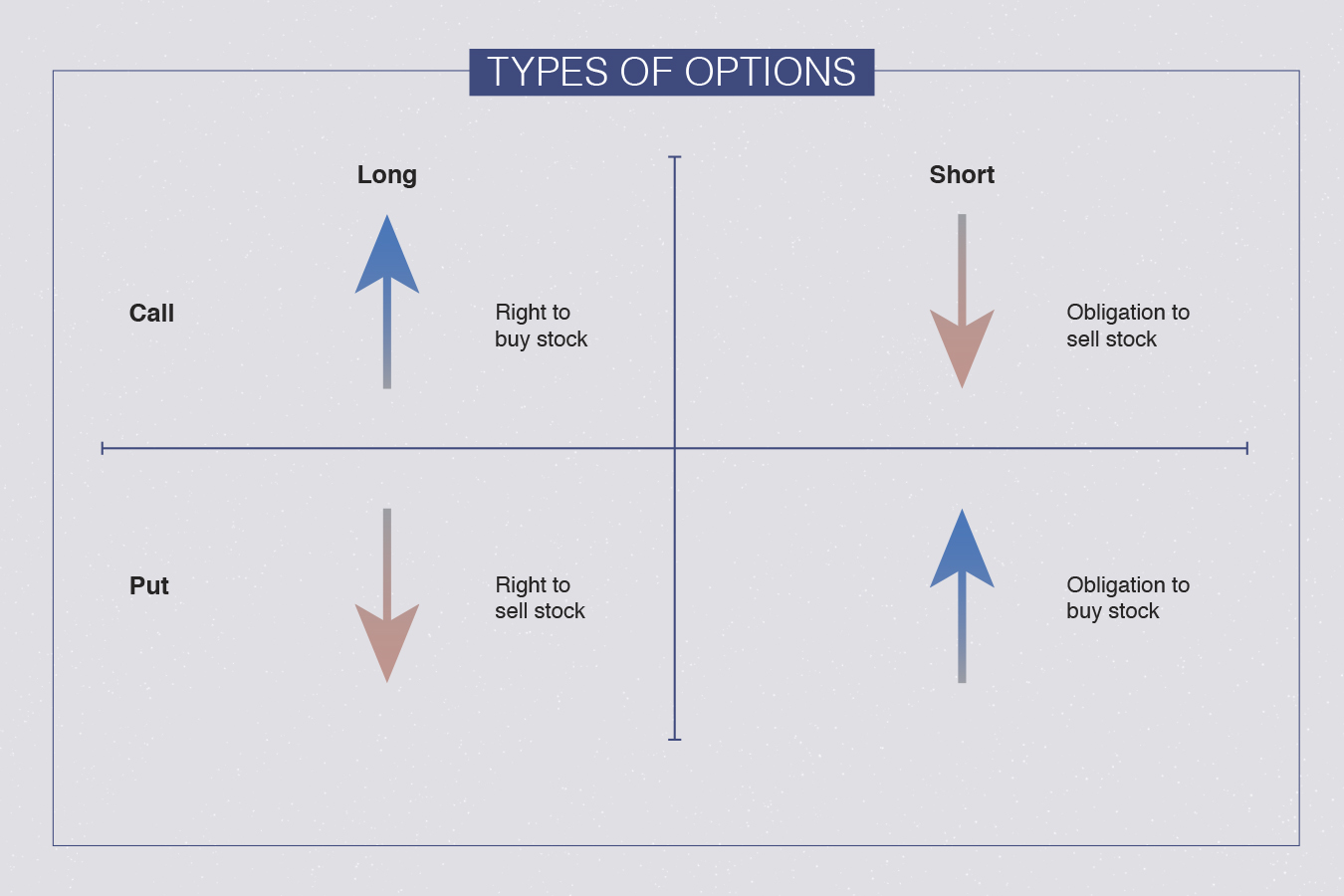
What to be familiar with put choices: can be purchased/sold in light of your trading procedure and expectation of cost, accompany a strike cost and can make another investor or broker purchase/sell a security before choice lapses.
A put choice is to sell a security at a particular cost until a specific date. It gives you a choice to "put the security down." The option to sell security depends on an agreement. The protections usually are stocks yet can likewise be wares fates or monetary standards.
The particular cost is the "strike cost" since you will probably strike when the stock value tumbles to that worth or lower. What's more, you can sell it up to a settled upon date. That is known as the "lapse date" since that is the point at which your choice terminates.
Assuming you sell your stock at the strike cost before the termination date, you "work out" your put choice in an American choice. You can practice your put choice precisely on the termination date in a European choice.
Key Takeaways
- A put choice can make another financial backer or dealer trade security before the choice terminates.
- A put choice generally accompanies a strike value that you set to hold you back from losing beyond what you can bear.
- You can trade put choices in light of your exchanging technique and your expectation of the resource's cost.
Purchase
When you purchase a put choice, you're ensured not to lose more than the superior you paid to purchase that choice. You pay a little expense to the individual who will purchase your stock.
The expense covers their gamble. They understand you could request that they get it any day during the settled-upon period. They likewise understand that the stock could be worth a lot less on that day. However, they believe it's worth the effort since they accept the stock cost will rise. Like an insurance agency, they'd prefer to have the charge you offer them as a trade-off for the little opportunity they'll need to purchase the stock.
Long put:
If you purchase a put without possessing the stock, this is known as a long put.
Safeguarded put:
If you purchase a put on a stock you currently own, that is known as a safeguarded put. Likewise, you can purchase a put for an arrangement of stocks or trade exchanged reserve (ETF). That is known as a "protective index put."
Sell
You consent to purchase a stock at a settled-upon cost when you sell a put choice.
Put venders lose cash if the stock cost falls. They should purchase the stock at the strike value but can sell it at a lower cost. If the stock cost rises, they bring in cash because the purchaser won't practice the choice. The put vendors pocket the charge.
Put dealers stay in business by composing many puts on stocks they think will ascend in esteem. They trust the charges they gather will counterbalance an intermittent misfortune they cause when stock costs fall.
A put dealer can escape the understanding by purchasing a similar choice from another person. Assuming the charge for the new choice is lower than what they got for the ancient one, they pocket the distinction. They would possibly do this assuming they thought the exchange was conflicting with them.
A few merchants sell puts on stocks they might want to possess because they assume they are right now underestimated. They are glad to purchase the stock at the ongoing cost since they accept it will arise later. Since the purchaser of the put pays them the expense, they purchase the stock at a markdown.
Cash secured put deal:
You keep sufficient cash in your record to purchase the stock or cover the put.
Naked put:
This is when you sell a put unhedged. This choice system isn't covered with cash but instead by the edge.
Model Using Commodities
Put choices are utilized for products as well as stocks. Items are certain things like gold, oil, and farming items, including wheat, corn, and pork tummies. Dissimilar to stocks, items aren't traded inside and out. No investor or broker buys and takes responsibility for "pork belly."
All things being equal, items are purchased as fates contracts. These agreements are dangerous because they can open you to limitless misfortunes. Why? Not at all like stocks. You can't buy only 1 ounce of gold. A solitary gold agreement is worth 100 ounces of gold. If gold loses $1 an ounce the day after you purchased your agreement, you've recently lost $100. Since the agreement terminates from now on, you could lose hundreds or thousands of dollars when the agreement comes due.
Put choices are utilized in wares exchanging because they are lower risk for engaging in these hazardous items prospects contracts. In wares, a put choice gives you a choice to sell a fates contract on the hidden product. When you purchase a put choice, your gamble is restricted to the cost you pay for the put choice (called the top-notch) and any commissions and charges.
Indeed, even with the decreased gamble, most dealers don't practice the put choice. They use its protection to safeguard against misfortune. All things being equal, they close it before it terminates.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens when a put choice terminates?
If a put choice lapses before it is worked out, it vanishes. The business will eliminate that choice from the record of the individual who purchased the put. The individual who sold the put no longer needs to stress keeping up with the purchasing ability to buy the offers. Remember that businesses may naturally practice choices on the termination date, assuming they are in cash (ITM), so ITM choices will probably not lapse.
What happens when you practice a put choice?
When you practice a put choice, you (as the put choice purchaser) will offer 100 offers to the put choice dealer. If you don't possess the offers before practicing the choice, then, at that point, you'll require the purchasing ability to cover that buy — even though you may claim the offers for only minutes.
How would you close a put choice?
If you offered the put to open the exchange, you would purchase the put at the ongoing business sector cost to close it. On the off chance that you initially purchased the put choice, you will offer it to close the exchange. A choice's lapse or exercise will likewise close the exchange for the two players.
When would it be a good idea for you to purchase a put choice?
As a rule, you need to purchase a put choice when you negatively feel about security. All in all, purchase puts when you accept the stock's cost will go down. A few brokers use puts to fence different positions they hold. For instance, if somebody possesses a great deal of Apple, they might need to purchase an Apple put so they will not lose everything assuming Apple crashes.